A sunroof is no more a luxury addition only found in expensive vehicles. Sunroofs have been a sought-after addition in many different markets as demand for chic and feature-packed cars rises. Actually, studies show that more than 40% of mid-range SUVs and sedans sold in India now have a sunroof, either standard or optional. From improving the look of the interior to offering an airy, open-sky feel, a sunroof gives a sophisticated touch that Indian consumers yearn for.
The sunroof adds indisputable beauty, whether your main goal is more natural light within the cabin or the cool wind on picturesque journeys. Read on as we go over the best cars with sunroof in India in a range of budgets, to help you select the ideal ride that fits your taste and style.
List of Best Cars with Sunroof in India:
Here is a detailed list of the best cars with sunroof in India:
| Car | Transmission | Mileage | Ex-Showroom Price (lakhs) |
| Mahindra XUV700 | 6-speed MT and AT | 16.57 kmpl AT/ 17 kmpl MT (Diesel) and 13 kmpl AT/15 kmpl MT (Petrol)Airbags: 7 | Rs. 14.00 – 27.00 |
| Hyundai Creta | 6-speed MT/ 7-speed DCT/IVT (Petrol) and 6-speed MT/6-speed AT (Diesel) | 19.10 kmpl AT/ 21.80 kmpl MT (Diesel) and 18.40 kmpl AT/17.40 kmpl MT | Rs. 10.95 – 19.20 |
| Tata Nexon | 6-speed MT/6-speed AMT (Petrol and Diesel), 7-speed DCA (Petrol), and 6-speed MT (CNG) | 24.08 kmpl AT/ 23.23 kmpl MT (Diesel), 17.18 kmpl AT/17.44 kmpl MT (Petrol), and 17.44 km/kg (CNG) | Rs. 8.00 – 15.60 |
| Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara | 5-speed MT and 6-speed AT | 20.58 kmpl AT/ 20.62 kmpl MT (Petrol), 27.97 kmpl (Hybrid), and 26.6 km/kg (CNG) | Rs. 10.70 – 19.50 |
| MG Hector | 6-speed MT and CVT (Petrol)/ 6-speed MT (Diesel) | 12.34 kmpl CVT and 13.79 kmpl (Petrol)/ 15.58 kmpl (Diesel) | Rs. 15.00 – 22.12 |
| Kia Seltos | 6-speed MT/6-speed iMT/CVT (Petrol) and 6-speed MT/6-speed iMT/6-speed TC Automatic (Diesel) | 20.7 kmpl AT/ 20.7 kmpl MT (Diesel), 17.9 kmpl AT/17.7 kmpl MT (Petrol) | Rs. 10.89 – 20.49 |
| Hyundai i20 | 5-speed MT and iVT | 16 kmpl (MT)/20 kmpl (iVT) | Rs. 7.04 – 11.25 |
| Hyundai Verna | 6-speed MT and 7-speed DCT | 18.6 kmpl MT and 20.6 kmpl DCT | Rs. 10.89 – 17.37 |
| Tata Harrier | 6-speed MT/6-speed AT | 14.6 kmpl – 16.8 kmpl | Rs. 15.49 – 25.49 |
| Mahindra XUV3XO | 6-speed MT and Automatic (Petrol)/ 6-speed MT and AMT (Diesel) | 20.6 kmpl AT/ 20.6 kmpl MT (Diesel), 18.2 kmpl AMT/20.1 kmpl MT (Petrol) | Rs. 7.99 – 15.56 |
Mahindra XUV700
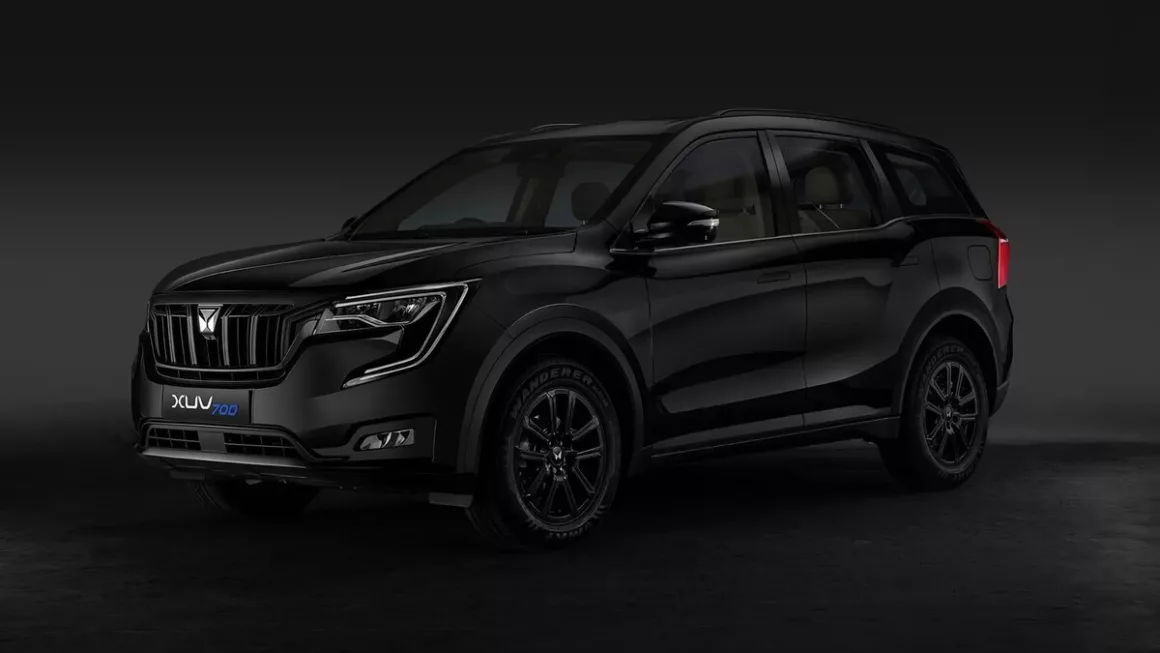
Refining the SUV experience in India, the Mahindra XUV700’s panoramic sunroof, rightly called the Skyroof, is among its most discussed characteristics. Stretching over the roofline, the Skyroof provides an open-air experience and floods the cabin with natural light. This function improves the already excellent cabin of the SUV, therefore increasing the enjoyment of long rides.
Mahindra has cleverly combined the sunroof across many models to make sure even mid-range consumers can savor the luxury of an airy cabin. The voice-controlled panoramic sunroof comes with an anti-pinch protection feature and automatically closes if rain-sensing wipers detect moisture. Families will find the XUV700 to be a whole package, including roomy cabins, a large touchscreen infotainment system, and superior upholstery. The Mahindra XUV700’s Skyroof is rather remarkable if you want a car that maximises comfort and provides an immersive driving experience.
Mahindra XUV700 Specifications:
- Engine: 2.0 L, 4-cylinder (Petrol) and 2.2 L,4-cylinder (Diesel)
- Transmission: 6-speed MT and AT
- Mileage: 16.57 kmpl AT/ 17 kmpl MT (Diesel) and 13 kmpl AT/15 kmpl MT (Petrol)
- Airbags: 7
- Fuel Type: Diesel and Petrol
- Seating Capacity: 5, 6, and 7-seater configurations
- Body Type: SUV
Mahindra XUV700 Key Features
- Expansive Skyroof for a premium open-air experience
- ADAS with lane-keep assist and adaptive cruise control
- Dual HD 10.25-inch screens with Android Auto & Apple CarPlay
- Bose premium sound system for an immersive audio experience
Hyundai Creta
Consistent in ruling the midsize SUV market, the Hyundai Creta’s panoramic sunroof is a big crowd-pulling feature. This sunroof is available in the SX and SX(O) variants. Hyundai has made sure the sunroof enhances the experience rather than being a luxury addition with its voice-enabled features. Whether you’re cruising down city streets or taking a weekend trip, the panoramic view adds a sense of openness, making every journey feel more refreshing.
Inside, the Creta contrasts its sunroof with a cosy, feature-packed interior. The 10.25-inch infotainment system enhances tech-savvy attractiveness; the dual-tone interiors, ambient lighting, and roomy layout guarantee comfort. The car comes with a hi-tech Bose sound system with Android Auto/Apple CarPlay compatibility and Home to Car (H2C) with Alexa. A one-year free subscription to JioSaavn is included too. Moreover, some of the safety features of Creta include ADAS functions, three-point seat belts, electronic stability control, hill start assist, all-disc brakes, blind-spot view monitor, surround view monitor, etc., are some of its safety features.
Hyundai Creta Specifications:
- Engine: 1.5L, 4-cylinder
- Transmission: 6-speed MT/ 7-speed DCT/IVT (Petrol) and 6-speed MT/6-speed AT (Diesel)
- Mileage: 19.10 kmpl AT/ 21.80 kmpl MT (Diesel) and 18.40 kmpl AT/17.40 kmpl MT
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol and Diesel
- Seating Capacity: 5
- Body Type: SUV
Hyundai Creta Key Features
- Panoramic sunroof for a spacious and airy cabin experience
- 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment system with Bose premium sound
- Ventilated seats and dual-zone climate control for added comfort
- Level-2 ADAS with features like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control
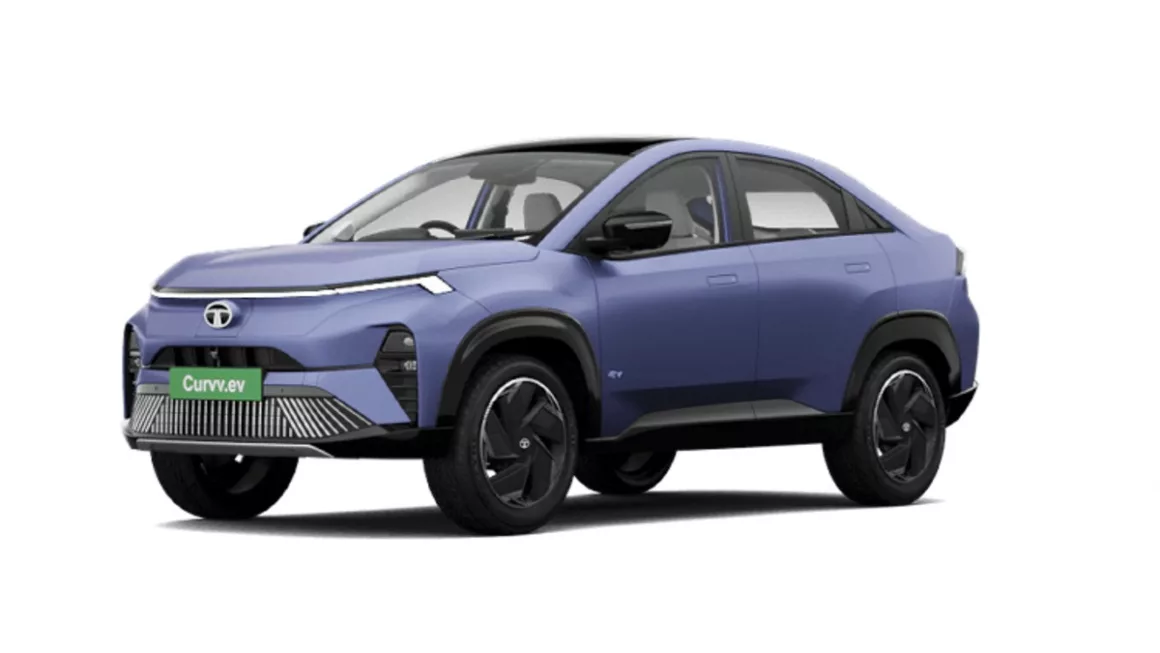
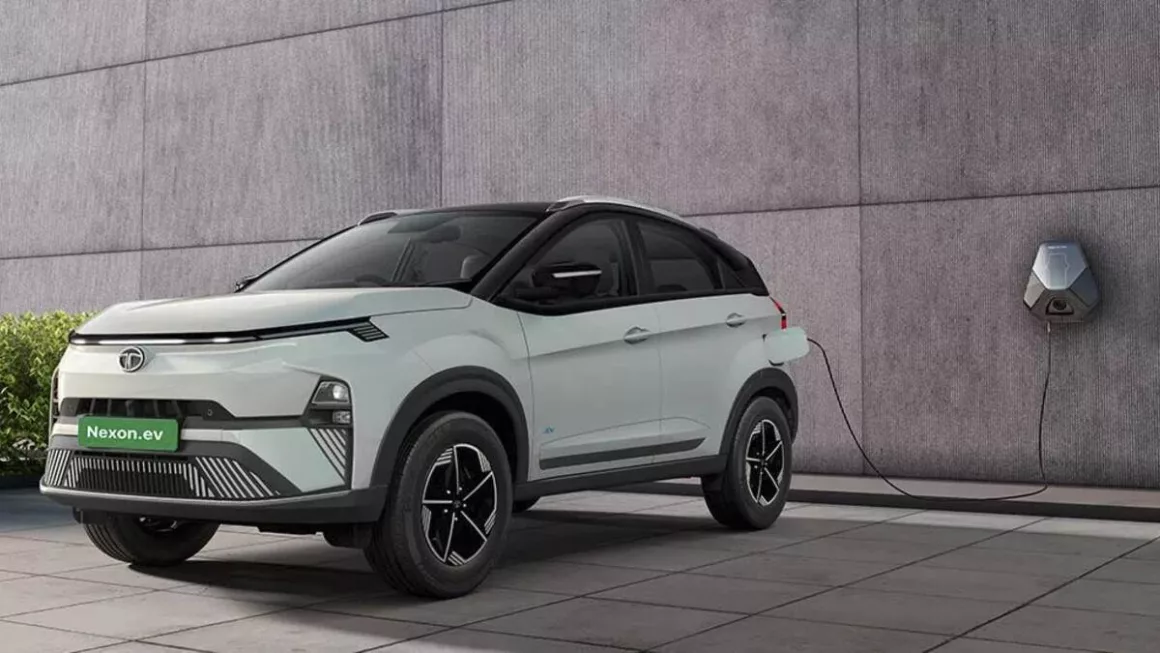
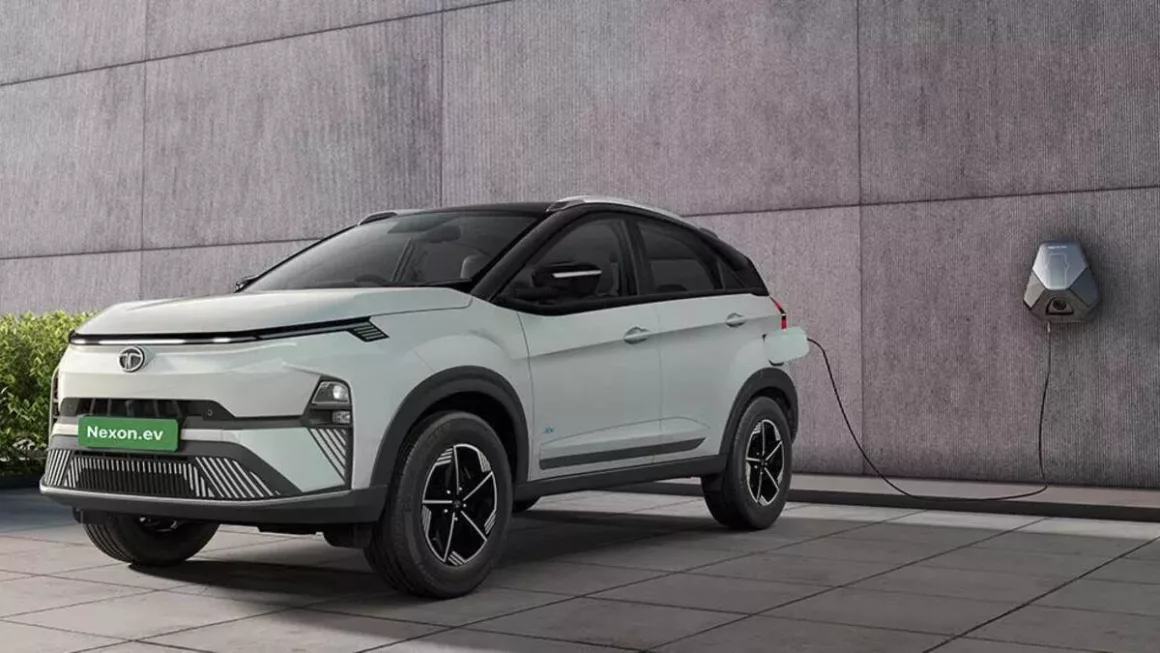
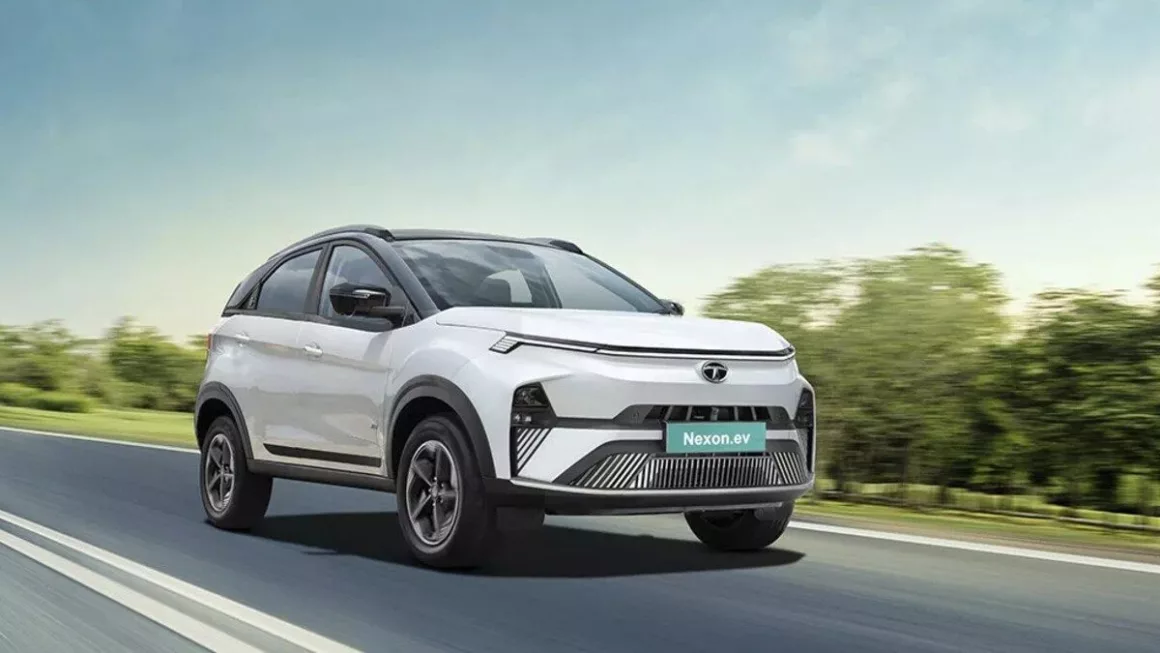
Tata Nexon
In the small SUV market, the Tata Nexon is becoming a household brand, and its electric sunroof is among its most appreciated features. Tata has guaranteed that even the mid-level models include this sunroof, therefore enabling a larger audience to enjoy this experience. The sunroof adds a premium feel to the already amazing cabin of Nexon. The electric sunroof operates via voice commands and comes with an air purifier to ensure air quality inside the cabin isn’t compromised.
The plush leatherette seats have under-thigh support in all rows. The infotainment screen by Harman and eight JBL speakers let you play your choice of tracks during the journey while sneaking a quick peek at your route via Google Maps. This car has received a 5-star safety rating in the BNCAP crash test, so that you can rest assured about safety. Even though it doesn’t have ADAS functionalities, features like blind-view monitor, auto headlamps, rain-sensing wipers, 360-degree surround view with front parking sensors, three-point seatbelts for all seats, rear defogger, auto-dimming IRVM, and more make the car safe and secure.
Tata Nexon Specifications:
- Engine: 1.2L 3-cylinder (Petrol and CNG)/ 1.5L, 4-cylinder (Diesel)
- Transmission: 6-speed MT/6-speed AMT (Petrol and Diesel), 7-speed DCA (Petrol), and 6-speed MT (CNG)
- Mileage: 24.08 kmpl AT/ 23.23 kmpl MT (Diesel), 17.18 kmpl AT/17.44 kmpl MT (Petrol), and 17.44 km/kg (CNG)
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol, Diesel, and CNG
- Seating Capacity: 5
- Body Type: SUV
Tata Nexon Key Features
- Electric sunroof with voice control for hands-free operation
- 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment with connected car technology
- Ventilated front seats for added comfort on long drives
- 360-degree camera for better visibility and parking assistance
- 7-speaker JBL sound system for an immersive audio experience
Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara
Offering an electronic panoramic sunroof in its Alpha and Zeta+ models, the Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara stands out in the mid-size SUV range. The panoramic sunroof ensures both front and rear passengers get to feel the “open-air” experience. Aimed to accentuate the feeling of room and elegance, the large sunroof floods the interior with natural light, therefore improving comfort and driving experience immersion.
Offering a dual-tone luxurious interior, a 9-inch SmartPlay Pro+ infotainment system, and ambient lighting, Maruti has painstakingly created the Grand Vitara to meet contemporary demands. The sunroof experience is even more enhanced for those choosing the robust hybrid powertrain with the SUV’s almost silent electric mode. Voice-activated controls also enable the simple opening or closing of the sunroof. What has truly resonated with SUV lovers is the AllGrip technology, which has made this car a favorite when it comes to off-roading. No wonder it has passed a milestone in just 2 years by selling 200,000 units in 2024!
Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara Specifications:
- Engine: 1.5L, 3-cylinder and 1.5L, 4-cylinder (Petrol)/ 1.5L, 4-cylinder (CNG)
- Transmission: 5-speed MT and 6-speed AT
- Mileage: 20.58 kmpl AT/ 20.62 kmpl MT (Petrol), 27.97 kmpl (Hybrid), and 26.6 km/kg (CNG)
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol and CNG
- Seating Capacity: 5
- Body Type: SUV
Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara Key Features
- Voice-activated sunroof control for added convenience
- 9-inch SmartPlay Pro+ infotainment system with wireless connectivity
- AllGrip AWD option for off-road enthusiasts
- 360-degree camera for enhanced safety and parking assistance
MG Hector
The MG Hector takes the SUV experience up a notch with its panoramic sunroof, available in the Smart, Sharp, and Savvy variants and is the biggest in its category. The dual-pane panoramic, voice command-operated sunroof lends a sense of openness and elegance, whether you’re enjoying city lights at night or passing breathtaking scenery.
Beyond the sunroof, the car also features an enormous 14-inch infotainment system, integrated with a 7-inch digital driver display, i-SMART connected technology that includes over 70 features, and 8 speakers. Other features include a 360-degree camera, ambient lighting, auto turn indicators, level 2 ADAS features, three-point seatbelts, ISOFIX child seat anchors, and disc brakes on all wheels.
MG Hector Specifications:
- Engine: 1.5L,4-cylinder (Petrol)/2.0,4-cylinder (Diesel)
- Transmission: 6-speed MT and CVT (Petrol)/ 6-speed MT (Diesel)
- Mileage: 12.34 kmpl CVT and 13.79 kmpl (Petrol)/ 15.58 kmpl (Diesel)
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol and Diesel
- Seating Capacity: 5, 6, and 7-seater configurations
- Body Type: SUV
MG Hector Key Features
- AI-powered voice assistant for hands-free sunroof operation
- 14-inch HD touchscreen infotainment system with wireless connectivity
- Ventilated front seats with premium leatherette upholstery
- ADAS features like lane-keep assist and adaptive cruise control
Kia Seltos
With its contemporary look and feature-loaded cabin, the Kia Seltos distinguishes itself among the small SUV market. The panoramic sunroof is included in the HTX+ and GTX+ models, adding elegance and improving the interior’s spaciousness. Additionally, the touchscreen and instrument cluster are packaged as one unit, while the Bose premium sound system lets you enjoy music or listen to podcasts as you drive. The segment-first SUV also includes ventilated front seats, a Connect app with live tracking, security alerts & remote start/stop/lock/unlock features, ADAS functions, 360-degree camera view, hill assist, etc.
The Seltos’ mood lighting, which syncs with the music to create an ambient environment, makes the panoramic sunroof experience even more pleasant at night. Overall, the car provides a well-rounded opulent experience together with ventilated front seats, a 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment system, and a Bose premium sound system.
Kia Seltos Specifications:
- Engine: 1.5L,4-cylinder (Petrol and Diesel)
- Transmission: 6-speed MT/6-speed iMT/CVT (Petrol) and 6-speed MT/6-speed iMT/6-speed TC Automatic (Diesel)
- Mileage: 20.7 kmpl AT/ 20.7 kmpl MT (Diesel), 17.9 kmpl AT/17.7 kmpl MT (Petrol)
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol and Diesel
- Seating Capacity: 5
- Body Type: SUV
Kia Seltos Key Features
- Ambient mood lighting for a premium cabin experience
- 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment system with Bose audio
- Ventilated front seats for enhanced comfort
- ADAS Level 2 with features like lane keep assist and adaptive cruise control
Hyundai i20
The Hyundai i20 is one of the most iconic vehicles in India, and it comes with an electric sunroof in the Asta (O) variant. Moreover, if comfort and safety are your top priority, you can’t go wrong with the Hyundai i20 integrated with smart features like a voice-enabled sunroof, Home-to-Car (H2C) with Alexa and Bluelink-connected functionalities, and a 10.25-inch HD touchscreen infotainment system with a Bose premium seven-speaker system, climate control, multi-phone Bluetooth connectivity, this vehicle has achieved incredible sales figures since its launch.
Front seats have proper cushioning and support, while legroom for rear passengers is fantastic. Safety specs include vehicle stability management, tyre pressure monitoring system, driver rear view monitor, impact-sensing auto door unlock, speed-sensing auto door lock, three-point seatbelts, emergency stop signal, and more.
Hyundai i20 Specifications:
- Engine: 1.2L, 4-cylinder
- Transmission: 5-speed MT and iVT
- Mileage: 16 kmpl (MT)/20 kmpl (iVT)
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol
- Seating Capacity: 5
- Body Type: Hatchback
Hyundai i20 Key Features
- 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment system with Bose audio
- Ambient lighting for a luxurious cabin experience
- Connected car technology with Hyundai Bluelink
Hyundai Verna
The reasons why many choose Verna as their go-to vehicle are its 5-star safety rating and long list of ADAS features. But on top of that, Verna is also the car to have a segment-first voice-enabled electric sunroof in the SX, SX(O), and S(O) variants. This sunroof creates a stellar, open, and airy aura. The infotainment system can be synced with your smartphone, while a toggle switch lets you transition between climate control and media. The Bose sound system, heated front seats, smart trunk system (automatic opening of the bootlid on approach, anti-lock braking system with EBD, ISOFIX child seat anchors, vehicle stability management, and three-point seatbelts, etc., offer protection and enhance convenience.
Long rides are more fun in the sedan with its 10.25-inch touchscreen entertainment system, Bose premium sound system, and ventilated seats. Features like 6 airbags, ADAS Level 2, and Electronic Stability Control (ESC) equally give safety first importance.
Hyundai Verna Specifications:
- Engine: 1.5L, 4-cylinder
- Transmission: 6-speed MT and 7-speed DCT
- Mileage: 18.6 kmpl MT and 20.6 kmpl DCT
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol
- Seating Capacity: 5
- Body Type: Sedan
Hyundai Verna Key Features
- Segment-first tech integration with smart voice commands
- 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment with Bose sound system
- ADAS Level 2 with multiple driver assistance features
Tata Harrier
Rising in the SUV market, the Tata Harrier boasts a panoramic sunroof that accentuates its opulence. It is available in the Pure Plus S, Pure Plus S Dark, and Adventure+ variants. Known as the “SkyDome,” it is among the biggest of its kind and offers a broad perspective of an expansive view of the sky and allowing ample natural light to flood the cabin. Its anti-pinch function and rain-sensing closing guarantee ease as well as safety.
With its 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment system, premium JBL sound system, and ventilated seats, the Harrier’s sunroof, ideal for everyone who wants the best of luxury amenities. With six airbags, ADAS Level 2 technologies, and a strong construction based on Tata’s Omega Architecture, derived from Land Rover’s D8 platform, safety is always on top.
Tata Harrier Specifications:
- Engine: 2.0L, 4-cylinder
- Transmission: 6-speed MT/6-speed Automatic
- Mileage: 14.6 kmpl – 16.8 kmpl
- Airbags: 7
- Fuel Type: Diesel
- Seating Capacity: 5
- Body Type: SUV
Tata Harrier Key Features
- Largest panoramic sunroof in the segment with SkyDome technology
- Anti-pinch and rain-sensing sunroof for added safety
- 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment with JBL sound system
- Land Rover-inspired architecture for robust performance
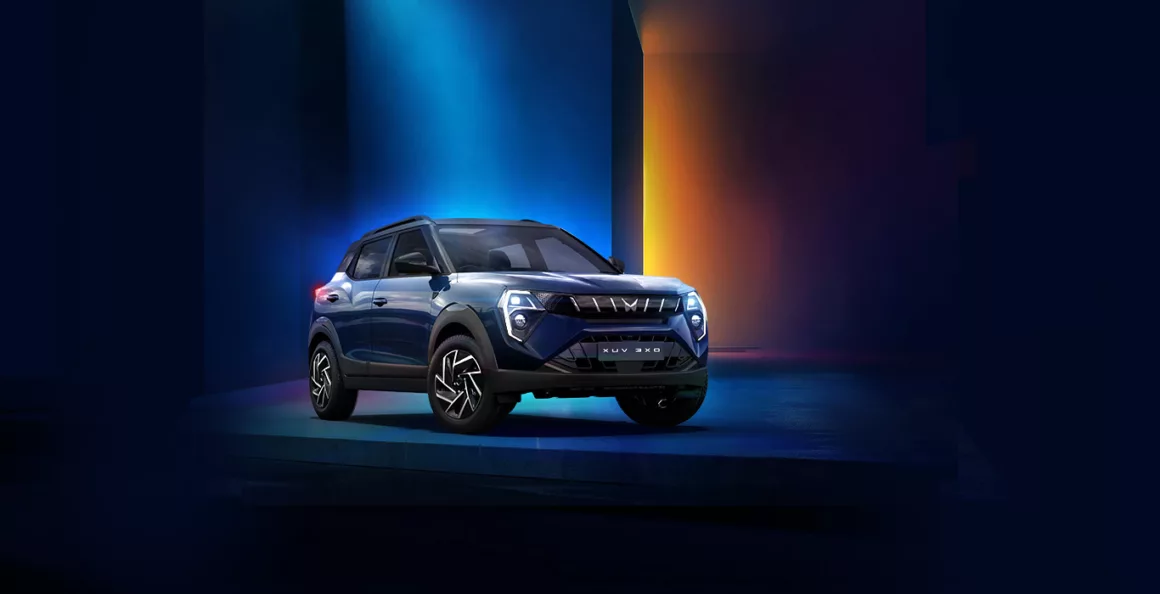
Mahindra XUV 3XO
The Mahindra XUV 3XO is one of the most trendy cars in the Sub-compact SUV market. This car boasts a panoramic sunroof in the MX2 Pro, AX5, AX7, and AX7L variants. It also comes with a level 2 ADAS safety package and has secured a 5-star rating in the BNCAP crash test. The interiors are spacious with features such as dual 10.25-inch infotainment screens, an electronic parking brake with auto-hold feature, and a 360-degree camera. The cooled glove box and dual-zone climate control are its USPs.
Complementing the sunroof, the XUV 3XO also has a premium Sony sound system, a 10.25-inch digital instrument cluster, and a 10.25-inch touchscreen infotainment system with wireless Android Auto and Apple CarPlay. With up to six airbags, ESP, and ADAS Level 2 for an extra piece of mind, safety is thoroughly addressed.
Mahindra XUV 3XO Specifications:
- Engine: 1.2L, 3-cylinder (Petrol)/ 1.5L, 4-cylinder (Diesel)
- Transmission: 6-speed MT and Automatic (Petrol)/ 6-speed MT and AMT (Diesel)
- Mileage: 20.6 kmpl AT/ 20.6 kmpl MT (Diesel), 18.2 kmpl AMT/20.1 kmpl MT (Petrol)
- Airbags: 6
- Fuel Type: Petrol and Diesel
- Seating Capacity:5
- Body Type: SUV
Mahindra XUV 3XO Key Features
- 10.25-inch dual screens with seamless connectivity
- Sony premium sound system for immersive audio
- ADAS Level 2 with advanced safety features
- Sporty turbocharged engines for dynamic performance
Summary:
Selecting a car with a sunroof not only lends a bit of elegance but also improves the driving experience by providing fresh air and natural light. Sunroof-equipped cars have become more common in India as manufacturers provide panoramic and electrically driven models in several models.
Think about your priorities if you’re looking for the ideal Indian car with a sunroof. The MG Hector and XUV 700 have a large panoramic sunroof for an opulent experience. The Hyundai Creta and Kia Seltos offer a great mix of features and style for a chic midsize SUV. If you want a sporty small car, the Hyundai i20 and Tata Nexon include sunroofs to provide an open-air sensation. For a sensible yet luxury experience, budget-conscious consumers should look at the Mahindra XUV 3XO or Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara. Each choice ensures a more enjoyable and connected drive.
FAQs
Q. Which are the best cars with sunroof in India?
If you prefer high-end vehicles, go for the BMW 3 Series, the Audi A4, and the Volkswagen Tiguan. Budget options include Kia Carens, Hyundai Creta, Mahindra Scorpio, and Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara.
Q. Can you add a sunroof to a car if it doesn’t have one?
Yes, sunroofs can be installed in vehicles that don’t include one. Still, you have to consider aspects like vehicle compatibility, type of sunroof, structural modifications, quality of materials, total cost, etc.
Q. What is the maintenance cost associated with a sunroof car?
Consult the manufacturer’s guide to find out about how you should utilize and maintain the sunroof. As long as the correct process is followed, you don’t have to worry about extra maintenance charges.
Q. What is the cost of a sunroof car in India?
The average cost of sunroof-integrated vehicles can start from Rs. 7 lakh and go up to over Rs. 1 crore, depending on the make and model.
Q. Are the best cars with sunroof in India safe?
Sunroofs are generally equipped with built-in features that prevent unauthorized entry attempts. Kia Seltos, Tata Nexon, Hyundai Verna, and Mahindra XUV 3XO come with impressive safety features to minimise break-ins and thefts.






 ne big family!
ne big family!
































































