With summer fast approaching, the dreaded heat and high temperatures are driving people to adopt all kinds of measures, including window sun shades, to tackle the heat while driving. But with several news articles and social media videos showing various state traffic police agencies launching drives to curb the use of window sun shades with heavy penalties and challans, it is easy for you to wonder whether these window sun shades are legal. Well, the answer is complicated, but fret not, as we are here to help. In this article, we have unravelled the mystery behind the legality of car window sun shades in India.
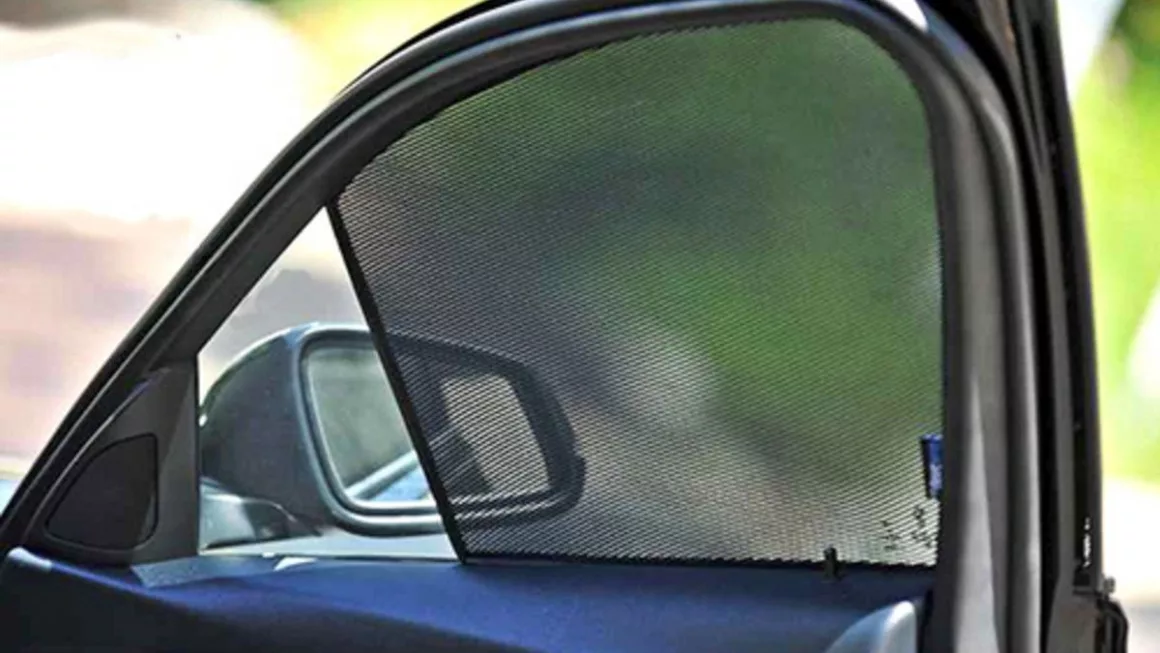
What is a Car Window Shade?
While tinted glasses and black films attract pricy challans and penalties, car window shades come in as an alternative to provide respite from the scorching summer heat and damaging UV rays that car passengers are subjected to while on the go. Made from different types of materials such as nylon, net fabric, mylar, aluminium foil, etc, car window shades are cutouts or pullovers that cover the windows and sometimes even the windshield of your vehicle to both reflect and absorb sunlight to reduce cabin temperature and UV rays penetration. The efficacy and effectiveness of a car window sun shade depend on the material it is made up of and its overall transparency. In addition to cooler cabin temperature and protection from UV rays, car window sun shades also help maintain the car interiors and prevent the steering from getting too hot. But despite these advantages, whether or not a car window shade is legal is what needs to be addressed before purchasing a shade for your car.
Is a Car Window Shade Legal?
While there is no doubt behind the illegality of tinted windows and black films, car window sun shades are often placed in the grey area of the law on motor vehicle visibility. Considered legal by a majority of the population, car window sun shades are used by millions of people across the nation, especially in areas that experience hotter summer months and prolonged sunlight. However, coming to the million dollar question, is a car window sun shade legal? When seen from a general perspective, anything that blocks the visibility of a motor vehicle’s windows and windshield is considered absolutely illegal by the law. This means that curtains, sun-shades, black films and tinted glasses are all considered to be illegal and will attract heavy penalties and challans. A common misconception here is that factory-fitted rollover sun shades, often seen in high-end luxury cars, are legal since they come directly from the manufacturer; however, in reality, even those shades are illegal and can be penalised by traffic officials. But if you are still wondering why car window sun shades are considered illegal, here is more about the law that governs the use of these shades and curtains.
Law Regarding Car Window Shades
When it comes to motor vehicles in India, the Motor Vehicle Act, 2019 and the Central Motor Vehicle Rules 1989 as Amended from time to time, govern and regulate every aspect of motor vehicles, including window visibility requirements.
As per Rule 100(3) of the Central Motor Vehicle Rules, 1989, “ The glass of the windscreen and rear window of every motor vehicle shall be such and shall be maintained in such a condition that the visual transmission of light (VLT) is not less than 70%. The glasses used for side windows are such and shall be maintained in such condition that the visual transmission of light is not less than 50% and shall conform to the Indian Standards”
This means that every motor vehicle in India shall maintain a visual transmission of light of 70% and above for the windshield and 50% and above for the windows. Visual transmission of Light means the percentage of light that can enter the vehicle through the glass. Thus, a windshield cannot block more than 30% of the light, and the windows cannot block more than 50% of the light.
However, this rule serves as the framework for OEM glass manufacturers for manufacturing safety glasses for motor vehicles in India. Only an OEM glass that abides by the said rule can attain the status of being RTO-approved and capable of being fitted in motor vehicles in India. Following the prescribed law, several car manufacturers, such as Maruti, are now using Asahi India Glass’s (AIS) Dark Green UV cut glasses to provide a legal alternative to the use of tinted glass and for the reduction of in-cabin heat and UV radiations. But all this still leaves sun-shades in a bit of a grey area.
When it comes to sun-shades and curtains, manufacturers and small-scale retailers often use Rule 100 of the CMVR to market their products as legal and confirming to the Visual Transmission of Light requirements. However, what they do not tell you is the fact that the Hon’ble Supreme Court had in 2012 ruled that the use of black films, tint, shades, curtains or any other material upon the widows or windshield of a vehicle that blocks visibility irrespective of its Visual Light Transmission percentage is absolutely illegal and the same had been brought in effect throughout the nation with effect from 4th of May 2012. Therefore, long story short, the use of car window sun shade is totally illegal in India.
State-wise Laws Regarding Car Window Shades
With the Hon’ble Supreme Court Ruling declaring the use of any material that blocks light on the safety glass of a vehicle to be illegal, the law is now universally applicable to all states of India. As a result, several states, such as Delhi, have also amended their state motor vehicle rules to incorporate the said guidelines and rulings.
As per Rule 114 of the Delhi Motor Vehicle Rules, “The glass of the front windscreen, and side and rear windows of every motor vehicle shall be such and shall be maintained in such a condition as to be clearly transparent and allow the driver a clear vision to the front and to the sides and through the prescribed mirror to the rear of the vehicle.”
FAQs
Q. What are car sun shades?
Made from different types of materials such as nylon, net fabric, mylar, aluminium foil, etc, car window shades are cutouts or pullovers that cover the windows and sometimes even the windshield of your vehicle to both reflect and absorb sunlight to reduce cabin temperature and UV rays penetration.
Q. How much tint is allowed in car windows and windshields?
As per Rule 100 of the Central Motor Vehicle Rules, every motor vehicle in India shall maintain a visual transmission of light of 70% and above for the windshield and 50% and above for the windows. Thus, a windshield cannot block more than 30% of the light, and the windows cannot block more than 50% of the light. However, this rule serves as the framework for OEM glass manufacturers for manufacturing safety glasses for motor vehicles in India.
Q. Is car sun shade legal in India?
No, as per the Supreme Court Ruling in 2012, car sun shades, curtains, black films, tinted glasses or any other material on the windshield or windows of a motor vehicle that blocks any amount of light is completely illegal.
Q. Can I use sun shades that block only 50% of light for my car windows?
No, the Visual Light Tranmsision norms that allow 50% light blockage for car windows are only for OEM safety glasses approved by the RTO, as per the Hon’ble Supreme Court’s ruling the use of black films, tint, shades, curtains or any other material upon the widows or windshield of a vehicle that blocks visibility irrespective of its Visual Light Transmission percentage is absolutely illegal.






 ne big family!
ne big family!













